Striped Maple: 7 Must-Know Buying Tips

Looking for a small, shade-loving tree with eye-catching stripes on its trunk? Striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum) fits the bill. It prefers cool, moist spots with partial to full shade. This post gives seven practical buying tips to help you pick healthy plants or seeds, place them in the right spot, and welcome local wildlife.
Table of Contents
Learn how to grow and use striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum) with practical steps that work in real gardens. This guide covers striped maple acer pensylvanicum identification, buying tips, siting, care, and wildlife value so you plant with confidence.
What Is Striped Maple (Acer pensylvanicum)?
Physical Characteristics and Identification
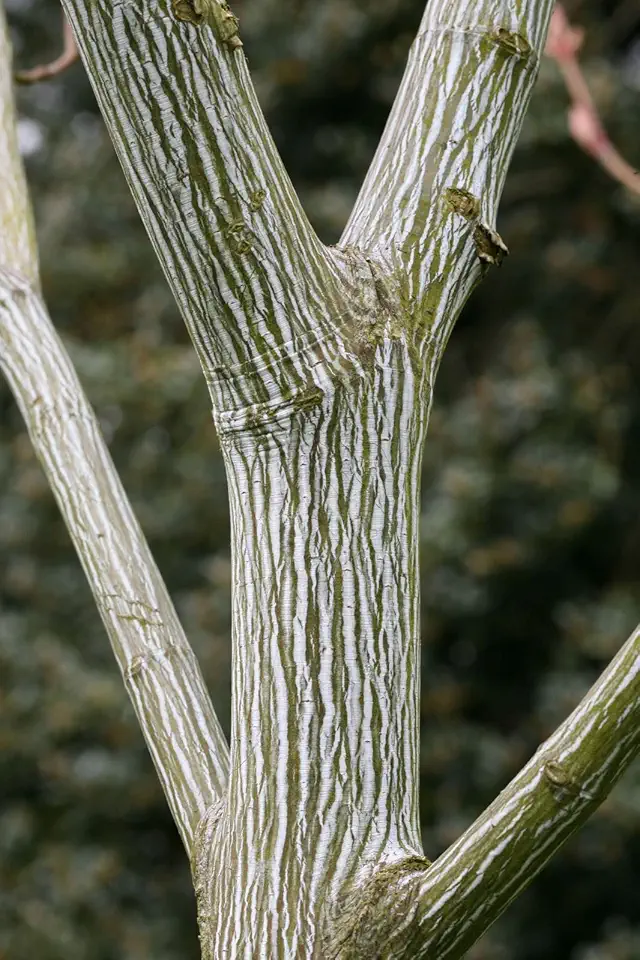
Spot striped maple by its green bark lined with vertical white stripes, three-lobed “goosefoot” leaves, and drooping chains of winged seeds. It’s also called snakebark maple, moosewood, goosefoot maple, and whistlewood; see traits and sizes below for quick ID (Mt. Cuba Center plant profile).
| Trait | Details |
|---|---|
| Mature height | 15–25 ft (rarely to 40 ft) |
| Mature spread | About 15 ft |
| Form | Broad, oval, sometimes shrub-like; slow growth |
| Bark | Green with white stripes on young wood; ages to reddish brown |
| Leaves | Large, 3-lobed; pinkish spring flush, deep green summer, bright yellow fall |
| Flowers | Small yellow-green racemes, April–May |
| Fruit | 1 in samaras in pendulous chains, summer maturing |
| Light | Partial to full shade |
| Soil | Moist, well-drained, slightly acidic; sandy loam preferred |
| USDA Zones | 3–7 |

Native Range and Hardiness Zones
This species is native to eastern North America, broadly from the Upper Midwest through the Northeast and down the Appalachian Mountains. It’s hardy in USDA Zones 3–7 and prefers cool, shaded slopes with steady moisture.
Zones 3–7 and cool, moist forest habitats define the sweet spot for Acer pensylvanicum.
USDA Forest Service
Growth Habits and Mature Size
Expect a slow-growing, understory tree that tops out around 15–25 feet with a similar, spreading width. Plan its placement like other shade-loving types of maple trees so roots stay cool and foliage avoids harsh sun.
1. Source Quality Plants or Viable Seeds
Choose Healthy Nursery Stock
Pick young trees with a straight leader, evenly spaced branches, firm buds, and no trunk wounds. Check for a fibrous, unstressed root system by teasing the soil surface; avoid pot-bound plants with circling roots or dry, hot containers.
- Ask for shade-grown stock to reduce transplant shock.
- Look for green, living cambium if a twig is lightly nicked.
- Choose containers that match root size (no “one size up” cramming).
- Reject trees with leaf scorch or wilt from sun exposure.
Select Properly Stratified Seeds
For seed propagation, buy fresh seed labeled cold stratified or start stratification yourself for 90–120 days at 34–41°F (1–5°C). Sow in late winter to early spring in a shaded frame using a moist, well-drained mix; keep the seedbed cool and evenly moist for steady germination.

20 Striped Maple Seeds (Acer pensylvanicum)
- Pack of 20 striped maple seeds for planting and propagation
- Ideal for native plant gardens and habitat restoration
- Best results with cold stratification before sowing
- Compact packaging protects seeds during shipping
- Great choice for gardeners and conservation projects
2. Evaluate Light and Shade Requirements
Partial to Full Shade Only
Place striped maple where it gets morning light and bright shade or dappled woods light the rest of the day. Midday sun burns foliage and stalls growth, so favor north- or east-facing exposures (see Gardening Know How on striped maple).
Avoid Sun-Exposed Locations
Skip open lawns, hot patios, and south-facing slopes that amplify leaf scorch. Tuck the tree into a woodland edge, behind taller canopy trees, or near buildings that cast afternoon shade without crowding roots.
- Use shade from oaks, beeches, or hemlocks as a living umbrella.
- Plant 6–10 ft inside a woodland margin for reliable dappled light.
- Mulch 2–3 in deep to keep the root zone cool in summer.
3. Assess Site Conditions and Soil Needs
Moisture and Drainage Requirements
Provide consistent, even moisture in a well-drained site; water deeply during dry spells and avoid soggy soil. In naturalized beds, a wide mulch ring reduces evaporation and moderates soil temperature (Ohio DNR plant notes).
Soil pH and Composition
Slightly acidic, sandy loam suits this maple best, though it adapts to many forest soils if drainage is sound. If your soil runs alkaline, top-dress yearly with leaf mold or pine fines to nudge pH and build organic matter.
Climate Considerations
Striped maple favors cool microclimates with 90–210 frost-free days and steady precipitation. In warm regions, plant on north-facing slopes, add summer irrigation, and keep a permanent mulch to protect roots.
4. Plan for Mature Size and Spacing
Height and Spread Expectations
Expect about 15–25 feet in height and roughly 15 feet in spread, with a broad, irregular crown. Give young trees room for side branching so the striped bark stays visible from multiple angles.
Spacing From Structures
Plant at least 12–15 feet from walls, patios, and utility lines to reduce pruning and heat stress. Keep lawn irrigation heads away from the trunk to limit mechanical damage and wet bark.
Woodland Grouping Considerations
In woodland gardens, group two or three trees for layered, dappled shade without overcrowding. Mix with ferns and spring ephemerals so the bark and yellow fall color pop; for wood aesthetics inspiration, browse maple wood looks used in design.
5. Verify Species Authenticity
Confirm Scientific Name
Always check the tag for the exact name Acer pensylvanicum (note the single “n” in pensylvanicum). Don’t accept generic “snakebark maple” labels, since multiple Asian species share that common name.
Check Plant Origin
Ask suppliers about provenance if you’re restoring native habitat or matching local genetics. Request paperwork on seed source or nursery propagation, especially for conservation projects.
Avoid Species Confusion
Don’t confuse striped maple with decorative wood terms like tiger figure found in other maples. If you’re shopping for lumber, verify species and grading; learn how figure names differ by reading about tiger maple wood.
6. Understand Seasonal Ornamental Value
Year-Round Bark Interest
The main show is the striped bark—green with crisp white pinstripes on young trunks and stems. Place the tree where low winter sun grazes the bark, or up-light it with a soft, cool LED to highlight texture without heat.
Spring Flowers and Fall Color
In spring, dangling racemes of yellow-green flowers attract pollinators, followed by chains of winged samaras in summer. Leaves shift to a clear, bright yellow in autumn, especially in cool nights with steady soil moisture.
Landscape Applications
Use striped maple as a shade accent in small gardens, a focal understory tree in woodland borders, or a naturalized grouping along cool slopes. For design ideas that pair figured woods with living specimens, explore curly maple and ambrosia maple finishes used in outdoor structures.
7. Consider Wildlife and Ecological Benefits
Native Wildlife Support
Striped maple provides browse and cover in shaded forests, feeding parts of the food web from insects to larger mammals. Its role as an understory species contributes to layered habitat structure (USDA Forest Service species guide).
Habitat Restoration Uses
Plant it in cool valleys, ravines, and north-facing woods during restoration work to rebuild shade layers and stabilize understory diversity. Pair with native ferns and spring ephemerals to fill seasonal gaps and suppress invasive seedlings.
Companion Planting Options
Good companions include Solomon’s seal, wood aster, wedge-petal trillium, woodland phlox, and wild ginger. These plants like the same moisture, soil, and shade profile, helping you build a cohesive woodland bed.
Related Striped Maple Products
Decorative Wood Inlays
Woodworkers seeking a striped look often use specialty veneers and inlay strips for instruments and furniture. Compare species figures to your project palette; for general characteristics, review our guide to quilted maple wood.
Here are popular inlay options inspired by striped patterns that suit detailed work:

Black Striped Maple Inlay — 3/16 in
- Premium black maple veneer for decorative accents
- Precise 3/16 in width for clean inlay lines
- Easy to cut and glue for woodworking projects
- Adds striking contrast to instruments and furniture
- Durable finish that sands and polishes well

Black Zebrawood Maple Inlay — 5/16 in
- Bold zebrawood striping for eye-catching inlay work
- Generous 5/16 in width for strong visual impact
- Easy to trim and fit in grooves or edges
- Ideal for guitars, furniture, and decorative projects
- Holds up well to sanding and finishing
Craft Materials
Confirm species and source for any craft lumber sold as “striped maple,” since figure names vary across maples. For gardens and habitat work, stick to live plants or seed labeled “striped maple acer pensylvanicum” so your planting matches the native species and your search intent for striped maple stays precise.
FAQs
What Is The Habitat Of Striped Maple Trees?
Striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum) thrives in cool, moist, shaded understories of temperate forests, especially in the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. It prefers well-drained, acidic soils rich in organic matter and is commonly found on north-facing slopes, ravines, and along stream banks where temperatures are moderate and light is filtered.
How Can I Identify A Striped Maple?
Striped maples are small trees or large shrubs, typically 10–25 feet tall, notable for their distinctive green bark marked with vertical pale or white stripes. Leaves are large, three-lobed, opposite, and turn bright yellow in fall; the tree also produces paired samara seeds. Look for the striped bark, lobed opposite leaves, and a multi-stem or branching habit to confirm identification.
Are Striped Maples Good For Landscaping?
Yes — striped maples can be excellent for shaded or woodland gardens because of their compact size, attractive striped bark, and bright fall color. They work well as understory specimens, in native plantings, or naturalized settings. Note they prefer moist, shady sites and can be sensitive to hot, dry conditions and heavy sun; they may also be browsed by deer, so site selection and protection are important.
Why Do Striped Maple Leaves Turn Yellow?
Leaves naturally turn yellow in autumn as part of seasonal senescence. If yellowing occurs prematurely, common causes include nutrient deficiencies (especially nitrogen or iron), poor drainage or overwatering, root stress or damage, compacted soil, or certain diseases and pests. A soil test, proper watering, mulching, and addressing any root or pest issues can help diagnose and correct abnormal yellowing.
Do Striped Maples Have Any Ecological Benefits?
Yes — striped maples provide habitat and food for wildlife: their foliage supports caterpillars and other insects, their seeds are eaten by birds and small mammals, and the dense understory growth offers cover for birds and small animals. As a native understory species, they also contribute to forest biodiversity, help stabilize soil, and support local ecosystem functions.